The Gluten Free Craze
- At February 06, 2014
- By Katherine
- In Articles, News
 0
0
Do you need Gluten Free? 29% of Americans are trying to avoid gluten… Gluten free food has grown to a $4 billion industry
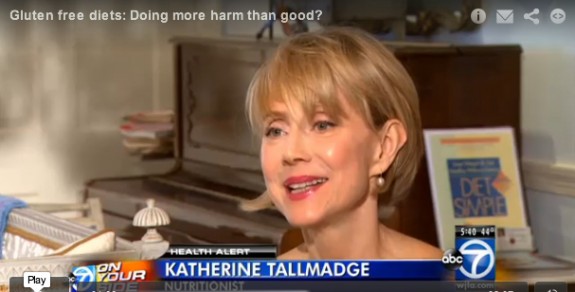
See me explain how a gluten-free diet may do more harm than good by clicking above or on ABC-7
This article appeared in The Huffington Post
Hear me – and three other experts – discuss “The Gluten-Free Craze” on National Public Radio’s The Diane Rehm Show.
It’s all the rage right now; in fact, you may be thinking of going on a gluten-free diet. Before you do, here are some things to think about:
First, you are likely to miss out on critical nutrients and health benefits only gained with gluten-containing whole grains (see below for the list). Most of those studies you’ve heard about proving the benefits of whole grains have used gluten-containing wheat, America’s (and the Mediterranean Diet’s) staple grain.
Second, a gluten-free diet is a therapeutic diet for those with debilitating celiac disease, a serious auto-immune disorder which virtually destroys the intestinal tract. But celiac only affects about 1% of the population.
Third, the danger of self-diagnosing and taking gluten out of your diet prematurely is that you will would never be able to get an accurate diagnosis of your symptoms. An intestinal biopsy is the only way to detect celiac definitively.
People try a gluten-free diet because they are overweight, feel tired, bloated, and/or depressed, and find reducing gluten correlates with feeling better or losing weight. But that is more likely because they’ve cut out excess calories found in many flour-based snack foods and sweets. They mistakenly attribute feeling better to taking out gluten.
Fourth, gluten-free diets can be seriously nutrient-deficient, low in fiber, iron, folate, niacin, thiamine, riboflavin, calcium, B12, phosphorus, and zinc. That’s because so many “gluten-free” products are made with refined, unenriched grains and starches, which contain plenty of calories, but very few vitamins and minerals.
The new $4 billion gluten-free industry is taking advantage of Americans’ desperation to feel better and lose weight. There has been an explosion of gluten-free junk foods, which has fueled this trend, and I hope you don’t become a victim.
But I have great news… many clients have thought they might need a gluten-free diet, but when we worked together at improving their nutrition and life balance, symptoms vanished! Perhaps that could be you? If you take the following steps and find you do need a gluten-free diet, it can fill all your nutritional requirements, but only if done CAREFULLY…
Do You Need A Gluten-Free Diet? A Step-by-Step Guide
1. Have a complete check-up with your family physician,
2. Consult with appropriate specialists, such as an allergist for wheat allergy and a gastroenterologist for celiac or another GI disease, A. If you have a wheat allergy, you must avoid wheat, but you do not have to avoid gluten from other grains, B. If you have celiac disease, you must avoid gluten – even the tiniest amounts (you must be eating gluten for the diagnosis to be made),
3. If you do not have a wheat allergy or celiac, visit a registered dietitian to verify that you are eating a balanced diet with plenty of nutrient-dense, naturally fiber-rich foods and adequate physical activity. A healthy diet and lifestyle reduces negative gastrointestinal symptoms, inflammation, boosts the immune system, improves brain function, reduces depression, and anxiety. If you are overweight, lose weight, as body fat can be toxic and produces hormones and pro-inflammatory chemicals which regulate metabolism, the immune system, inflammation, and the progression of artery hardening, so that when you have less body fat, you get many biological benefits, and feel better,
4. If symptoms persist, though in most cases they do not, you may be one of the rare people who are “gluten sensitive.” To confirm the diagnosis, and if a gluten-free diet is absolutely necessary for you – even though a gastroenterologist has verified you do not have celiac disease – visit your gastroenterologist, or the University of Maryland’s “Center for Celiac Research,” where they specialize in, among other things, detecting “gluten sensitivity,” which may be a newly identified disorder.
What is Gluten?
Gluten is a protein in wheat and some other grains, such as rye and barley. A gluten experiment in Food Science at the University of Maryland left a lasting impression on me about the function and importance of gluten. I kneaded bread dough under flowing water. As I kneaded the dough, the starch slowly washed away. What remained was a rubbery mass – the gluten – the protein in wheat which gives bread its structure.
Gluten-Containing Foods
Barley, Bulgur, Cereal Binding, Couscous, Durum, Einkorn, Emmer, Filler, Farro, Graham Flour, Kamut, Malt, Malt Extract, Malt Flavoring, Malt Syrup, Oats which are not labeled “Gluten-Free” because they have been contaminated by gluten in the field or in the processing plant, Rye, Semolina, Spelt, Triticale, Wheat, Wheat Bran, Wheat Germ, Wheat Starch, and others…
Naturally Gluten-Free Whole Grains
Eat these instead of buying processed “gluten free” foods.* Brown Rice, Whole Corn, Gluten-Free Oats, Millet, Teff, Sorghum, Wild Rice, Buckwheat, Amaranth, and Quinoa.*
Wheat Allergy
WA is an adverse immunologic reaction to wheat proteins, a classic food allergy affecting the skin, gastrointestinal tract or respiratory tract.**
Celiac Disease
CD is an immune-mediated enteropathy (intestinal disease) triggered by the ingestion of gluten in susceptible individuals. The onset of symptoms is usually gradual and characterized by a time lag of months or years after gluten introduction.**
Gluten Sensitivity
When both allergic (WA) and autoimmune mechanisms (CD) have been ruled out (diagnosis by exclusion criteria), individuals who experience distress when ingesting gluten may be considered as having GS, though there is no definitive test for this diagnosis and it has not yet been proven by science that it exhists.* *
** “Spectrum of gluten-related disorders: consensus on new nomenclature and classification,” BMC Medicine 2012, 10:13 doi:10.1186/1741-7015-10-13; Sapone, Bai, Ciacci, Dolinsek, Green, Hadjivassiliou, Kaukinen, Rostami, Sander, Schumann, Ullrich, Villalta, Volta, Catassi, Fasano.
It is critical that you are examined by a gastroenterologist before switching to a Gluten-Free diet. Why? Once you eliminate gluten, it is virtually impossible to diagnose celiac, and the diagnosis of celiac, an extremely serious auto-immune disorder, should be your primary concern.
My Favorite Gluten-Free Guides
“Gluten-Free Diet: A Comprehensive Resource Guide” by Shelley Case, R.D.*
“Easy Gluten-Free” by Tricia Thompson, M.S., R.D. and Marlisa Brown, M.S., R.D.*
“Gluten-Free, Hassle Free” by Marlisa Brown, R.D., C.D.E.*
Anyone giving gluten-free dietary advice should be a registered dietitian, and have the “R.D.” after their name.
Don’t forget, Diet Simple is filled with recipes, including some marked “Gluten-Free!”
Hear me – and three other experts – discuss “The Gluten-Free Craze” on National Public Radio’s “Diane Rehm Show”…
See me explain how a gluten-free diet may do more harm than good by clicking above or on ABC-7
This article appeared in The Huffington Post
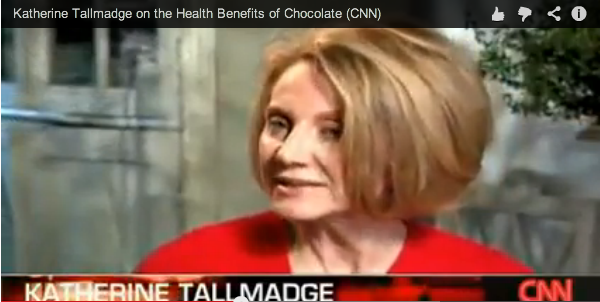
A Chocolate A Day? Chocolate Demystified
Is it true that a chocolate a day will keep the doctor away? Believe it or not, chocolate is among many of the healthiest foods. In fact, it has been shown to improve memory, decrease heart disease, heart attack, stroke, and diabetes risk! This is according to three decades of studies, culminating in this review of studies conducted so far, according to Nutrients Journal, and published in 2021
A Rich History
The cacao bean, grown mainly in Latin America, Africa and Asia, is loaded with beneficial compounds. In fact, its early uses, dating back 3,000 years were mainly medicinal. They have ranged from curing fatigue, angina, constipation, dental problems (tartar removal), dysentery, gout, an “overheated” heart, skin eruptions, fevers, and seizures. One doctor in the 1500s found it made people “extraordinarily fat” if used frequently and so it was prescribed for the thin and weak, according to an article in The Journal of Nutrition. It has been highly prized for centuries, which is reflected in its scientific name, Theobroma cacao, meaning “Food of the Gods.”
Eurpoeans discovered cocoa in the 1500s and over the next few centuries, chocolate, which we know and love so well was born. In this century, chocolate (processed cocoa with added fat, milk and sugar) has been enjoyed for its melt-in-your mouth texture and flavor, with its health giving properties largely forgotten by the civilized world, until recently.
In 1997, Harvard professor Norman K. Hollenberg published a landmark epidemiological study focused on cocoa. He found that high blood pressure was a rarity among Panama’s Kuna Indians who also didn’t experience the typical age-related increases. He at first attributed it to genetic protection. But, when the Kunas migrated to Panama City, their blood pressure increased, pointing to an environmental cause. Upon examination, Hollenberg found the Kunas drank large amounts of indigenous, unprocessed cocoa. Subsequent experiments conducted by Hollenberg and others, have found that cocoa, if high in flavanols, the beneficial plant compounds scientists believe impart most of cocoa’s benefits, relaxes the blood vessels, an important protection against hypertension and heart disease.
The Growth of Chocolate Research
Since Hollenberg’s findings, cocoa research has intensified, mainly due to the largess of companies like Mars, Inc, most famous for Milky Ways and M&Ms. What’s striking is that candy companies, such as Mars and Nestle’s, have hired respected nutrition scientists and have been largely responsible for the advancement of cocoa research. Mars has collaborated with such institutions as Harvard, the University of California at Davis, and even the United States Department of Agriculture’s Agricultural Research Service. Through their research and others, many interesting discoveries about cocoa’s health benefits have been made.
The flavanols in cocoa help maintain a healthy vascular system, relax blood vessels, they reduce blood clotting – an aspirin-like affect –reduce oxidative damage, and improve blood flow. A study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found cocoa also reduces inflammation. All of which reduces heart disease risk.
There have been some suggestion that flavanols can be used to treat vascular diseases like dementia, pre-eclampsia in pregnant women, and anything related to blood flow. Emerging research is looking into cancer as well.
But what about that chocolate bar in your vending machine? Are there any health benefits there? The answer: probably not much.
Most research about chocolate’s health benefits have used unsweetened cocoa or specially formulated high-flavanol chocolate. Unfortunately, these compounds are rarely in the chocolate we eat in 21st century America. Flavanols impart a bitter taste so they’ve been removed from most popular products to improve their flavor.
Most of the flavanols are in the cocoa beans and the level decreases with each processing step when it goes from the bean, to the cocoa powder and ultimately a finished chocolate product.
Since flavanols and their health benefits are a new discovery, chocolate companies are just beginning to see if there are ways to keep flavanols consistently high, but still have a tasty, popular product.
Katherine’s Chocolate-for-Health Tips
You’ll get more flavanols, and therefore health benefits, with less processing. The first choice is cocoa, which isn’t Dutch processed – as when cocoa is “Dutch processed with alkali” the flavanols are reduced. Look for chocolate which has the highest percentage of cocoa as possible and to save calories, look for chocolate with lower fat and sugar levels. In general, cocoa is your best first choice. Second choice is a semisweet or bittersweet chocolate with a high cocoa percentage. Some chocolates go as high as 85% cocoa, but legally can be as low as 35%. I recommend no more than an ounce a day, which may be about 110 – 150 calories, depending on the chocolate. Any more than that and you’re probably going to take in too many calories for weight control.
The numbers:
Type of Chocolate Mg Flavonols Calories
1.3 oz Dark Chocolate Bars, Average*: 82 mg 187
1.3 oz Milk Chocolate Bars, Average*: 42 mg 198
1 TBSP Unsweetened Cocoa Powder, Average*: 75 mg 12
*USDA’s Nutrient Data Laboratory
Use this incredible chocolate fondue recipe for berries, sliced pears, bananas, apples, pears, candied orange peels, and dried such as mangos, or any favorite fruit!
Katherine’s Hot Cocoa:
1 tsp or 1 Tbsp unsweetened cocoa, to taste
1 tsp or 1 Tbsp honey
1 cup Skim Milk or 1% Milk or Soy Milk
Heat in microwave for 2 – 3 minutes and stir to blend the chocolate.
Using 1 teaspoon of cocoa and sugar, contains approximately 25 mg flavanols and 115 calories (zero saturated fat), depending on the milk used.
Using 1 Tablespoon of cocoa and sugar, contains approximately 75 mg flavanols and 153 calories
Are you interested in chocolate’s health benefits? How much chocolate do you eat? Let me know in my “comments” section below…
Is it true that a chocolate a day will keep the doctor away? That’s what many chocolate companies would like you to believe in their Valentine’s Day advertisements. While it looks like cocoa has many health benefits, the chocolates you buy from your local stores may impart little of those benefits.
A Rich History
The cacao bean, grown mainly in Latin America, Africa and Asia, is loaded with beneficial compounds. In fact, its early uses, dating back 3,000 years were mainly medicinal. They have ranged from curing fatigue, angina, constipation, dental problems (tartar removal), dysentery, gout, an “overheated” heart, skin eruptions, fevers, and seizures. One doctor in the 1500s found it made people “extraordinarily fat” if used frequently and so it was prescribed for the thin and weak, according to an article in The Journal of Nutrition. It has been highly prized for centuries, which is reflected in its scientific name, Theobroma cacao, meaning “Food of the Gods.”
Eurpoeans discovered cocoa in the 1500s and over the next few centuries, chocolate, which we know and love so well was born. In this century, chocolate (processed cocoa with added fat, milk and sugar) has been enjoyed for its melt-in-your mouth texture and flavor, with its health giving properties largely forgotten by the civilized world, until recently.
In 1997, Harvard professor Norman K. Hollenberg published a landmark epidemiological study focused on cocoa. He found that high blood pressure was a rarity among Panama’s Kuna Indians who also didn’t experience the typical age-related increases. He at first attributed it to genetic protection. But, when the Kunas migrated to Panama City, their blood pressure increased, pointing to an environmental cause. Upon examination, Hollenberg found the Kunas drank large amounts of indigenous, unprocessed cocoa. Subsequent experiments conducted by Hollenberg and others, have found that cocoa, if high in flavanols, the beneficial plant compounds scientists believe impart most of cocoa’s benefits, relaxes the blood vessels, an important protection against hypertension and heart disease.
The Growth of Chocolate Research
Since Hollenberg’s findings, cocoa research has intensified, mainly due to the largess of companies like Mars, Inc, most famous for Milky Ways and M&Ms. What’s striking is that candy companies, such as Mars and Nestle’s, have hired respected nutrition scientists and have been largely responsible for the advancement of cocoa research. Mars has collaborated with such institutions as Harvard, the University of California at Davis, and even the United States Department of Agriculture’s Agricultural Research Service. Through their research and others, many interesting discoveries about cocoa’s health benefits have been made.
The flavanols in cocoa help maintain a healthy vascular system, relax blood vessels, they reduce blood clotting – an aspirin-like affect –reduce oxidative damage, and improve blood flow. A study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found cocoa also reduces inflammation. All of which reduces heart disease risk.
There have been some suggestion that flavanols can be used to treat vascular diseases like dementia, pre-eclampsia in pregnant women, and anything related to blood flow. Emerging research is looking into cancer as well.
But what about that chocolate bar in your vending machine? Are there any health benefits there? The answer: probably not much.
Most research about chocolate’s health benefits have used unsweetened cocoa or specially formulated high-flavanol chocolate. Unfortunately, these compounds are rarely in the chocolate we eat in 21st century America. Flavanols impart a bitter taste so they’ve been removed from most popular products to improve their flavor.
Most of the flavanols are in the cocoa beans and the level decreases with each processing step when it goes from the bean, to the cocoa powder and ultimately a finished chocolate product.
Since flavanols and their health benefits are a new discovery, chocolate companies are just beginning to see if there are ways to keep flavanols consistently high, but still have a tasty, popular product.
Katherine’s Chocolate-for-Health Tips
You’ll get more flavanols, and therefore health benefits, with less processing. The first choice is cocoa, which isn’t Dutch processed – as when cocoa is “Dutch processed with alkali” the flavanols are reduced. Look for chocolate which has the highest percentage of cocoa as possible and to save calories, look for chocolate with lower fat and sugar levels. In general, cocoa is your best first choice. Second choice is a semisweet or bittersweet chocolate with a high cocoa percentage. Some chocolates go as high as 85% cocoa, but legally can be as low as 35%. I recommend no more than an ounce a day, which may be about 110 – 150 calories, depending on the chocolate. Any more than that and you’re probably going to take in too many calories for weight control.
The numbers:
Type of Chocolate Mg Flavonols Calories
1.3 oz Dark Chocolate Bars, Average*: 82 mg 187
1.3 oz Milk Chocolate Bars, Average*: 42 mg 198
1 TBSP Unsweetened Cocoa Powder, Average*: 75 mg 12
*USDA’s Nutrient Data Laboratory
Use this incredible chocolate fondue recipe for berries, sliced pears, bananas, apples, pears, candied orange peels, and dried such as mangos, or any favorite fruit!
Katherine’s Hot Cocoa:
1 tsp or 1 Tbsp unsweetened cocoa, to taste
1 tsp or 1 Tbsp honey
1 cup Skim Milk or 1% Milk or Soy Milk
Heat in microwave for 2 – 3 minutes and stir to blend the chocolate.
Using 1 teaspoon of cocoa and sugar, contains approximately 25 mg flavanols and 115 calories (zero saturated fat), depending on the milk used.
Using 1 Tablespoon of cocoa and sugar, contains approximately 75 mg flavanols and 153 calories
Are you interested in chocolate’s health benefits? How much chocolate do you eat? Let me know in my “comments” section below…
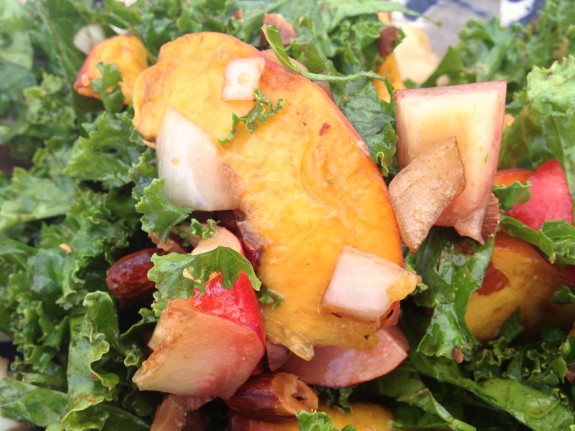
Farmers Market Recipe: Fresh Kale & Summer Peach Salad with Toasted Almonds & Balsamic Vinaigrette
- At July 19, 2013
- By Katherine
- In News, Recipes
 0
0
“I don’t normally like kale, but this salad is delicious!” is a comment I hear over and over when I serve this dish. Last year around this time, I was volunteering at an Anacostia Farmers Market. At the time, there was only one produce farmer at the market and all he had the day I was coming was peaches, kale and potatoes! My job at the Farmers Markets is to inspire people to buy the locally grown produce available that day, but what the heck was I going to do with kale, peaches and potatoes? I was stumped! Then I leafed through my own book, Diet Simple: 195 Mental Tricks, Substitutions, Habits & Inspirations, and got inspired by one of Chef Carla Hall’s contributions to my book, her “Hearty Greens Salad with Warm Balsamic Cherry Vinaigrette.” Aha! I can do a variation on the theme, I thought, use peaches, add some crunch with toasted almonds and VOILA! It was a HUGE HIT at the Anacostia Farmers Market. So I’ve included this wonderful recipe in my new book: Diet Simple Farm to Table Recipes (Bookbaby 2013)
Today is the 5th “Katherine’s Market Recipe” of 2013, all of which are designed to be delicious, easy, quick, famiy-friendly, nutritious (heart-healthy & diabetes-friendly), and to highlight produce found at our local farmers markets this week. At your farmers market, you’ll find produce picked at peak ripeness, which means maximum flavor, texture, and nutrition. You’re also helping save the environment when you buy at your farmers market. Here’s how…
Serves 6
Vinaigrette:
3 Tablespoons Extra Virgin Olive Oil
1 Tablespoon Balsamic Vinegar
Salt and Pepper to taste
Salad Ingredients:
6 Handfuls of fresh Kale (or other greens), washed, tough stems removed, and torn into bite-sized pieces
2 Cups Fresh Sliced Summer Peaches and/or any seasonal Berries
2 Ounces toasted slivered Almonds
½ Sweet Onion, peeled and sliced
In a large bowl, add the olive oil, vinegar, salt and pepper. Whisk together. Add the kale, onion, almonds, and peaches and toss together. Serve immediately.
Sieze the New Year!
- At January 05, 2013
- By Katherine
- In Articles, News
 0
0
What are your hopes, dreams and desires for 2013? The new year is a valuable opportunity to improve the quality of your life and happiness. Here’s how to make the best of it…
Now, move mindfully across the threshold into 2012 filled with ideas, possibilities and plans! Analyze people who will continue to be important, ideas to explore, places to spend time, important events and things to carry over from last year to this year.
CREATING A “SENSE OF URGENCY”
An important aspect to making major changes in the world or in your own personal habits is to feel a sense of urgency about your goal. A sense of urgency, according to The Dalai Lama in “The Art of Happiness” – and scholars in this important field of psychological research, can be achieved two ways:
1) Remind yourself of your positive vision for success. For example, visualize yourself at your goal weight, healthy, feeling energetic and confident (see “Dream” in my best-selling book, Diet Simple), and
2) Ponder the negative consequences of not making a particular behavior change (a little fear can be a good thing – but just a little). For instance, in the morning as you’re considering two options: getting out of bed to exercise or sleeping just a little longer. Ask yourself: “Do I want to feel good today? Or do I want to feel crummy today?” Another example, as you’re driving home from work and deciding to grab some carry-out or to go home to eat the healthy meal you’ve already planned. Ask yourself: “Do I want to achieve my weight loss goal (insert positive vision here) or will I accept being the same weight and having the same health problems for another year?” “Do I want to stop taking these darn medications or will I be taking them forever – and even increasing the dosage? What will my doctor say?” “What kind of example am I setting for my children, my spouse? Is this a behavior I can be proud of?” etc. You get the idea…
ACHIEVING INCREASED HAPPINESS
Outlining the consequenses of your actions and acting on your long term goals, as opposed to momentary desires, helps you grow as a person and become a happier person, according to scientific research. It increases your general happiness level because you are making decisions which contribute to your long-term goals.
THE DOWNWARD SPIRAL OF GIVING IN
Usually, when we do something that feels good momentarily, such as giving in and staying in bed for 30 more minutes of sleep in the morning instead of exercising, or grabbing a coffee cake at the coffee shop when we originally just planned on buying coffee, our happiness level may increase (“oooh, this feels yummy!”) – but it’s only a temporary blip of happiness. It goes back to the same level it did before – once the temporary experience wears off – and nothing changes for the better in our lives. We may even become more depressed as we continue to “give-in” to these unfulfilling momentary desires and continue into a downward spiral.
MAKING THE HARDER, BUT MORE SATISFYING CHOICE
If, instead, we say to ourselves, “I’m getting out of bed NOW! I’ll feel terrible if I don’t, and I’ll never achieve my goals,” or “Will stopping to get carry-out change my life for the better? I’d be better off going home and eating something healthy as I want to lose weight, lower my cholesterol, etc,” or “I really don’t need that coffee cake, and I’ll feel terrible after eating it, and will it make me happier at the end of the day?” “Will this increase my happiness for the short term? Or for the long term?” Another more extreme example might be a drug addict relapsing. It feels great momentarily, but the feeling doesn’t last.
When you make a more thoughtful decision, which contributes to your longterm health – physical or psychological – you are more likely to achieve your life’s hopes, dreams and goals, you can actually increase your happiness level, feel happier more often and grow as a person.
WHY IT’S NOT ALWAYS EASY
It is not always easy in our society to make the healthy decision. It’s easier – and the norm, in fact – to be overweight and unhealthy. But, I’m convinced it is possible to be healthy in an unhealthy world with planning, practice, determination, and support (I’m here any time you need me!) – Besides, what’s the alternative?
It takes effort to train your mind to work this way, but this is how we become better people and we advance as a society.
THE RESOLUTION SOLUTION:
HOW TO MAKE YOUR RESOLUTIONS SUCCESSFUL
“Forty to 50 percent of American adults will make New Year’s resolutions for self improvement. Scientific research indicates you are ten times more likely to change by making a New Year’s resolution compared to non-resolvers with the identical goals and comparable motivation to change,” says John C. Norcross, PhD, Professor of Psychology, University of Scranton and coauthor of “Changing for Good.”
Dr. Norcross recommends the following strategies, based on studies tracking successful New Year’s resolvers, and their differences with unsuccessful resolvers:
* Make realistic, attainable goals (See “Tiny Changes, Lasting Results” in Diet Simple’s Introduction),
*Develop a specific action plan (Fill out “Your Personal Goal Worksheet” in Diet Simple),
* Establish genuine confidence that you can keep the resolution despite the occasional slip. Confidence is a potent predictor of who succeeds in the new year! (creating your “sense of urgency” will be useful here – see above)
* Publicly declare your resolution. Public commitments are generally more successful than private decisions,
* Track your progress by recording or charting. Studies show self-monitoring one of the most important behaviors correlated with successful change (see “Write it to Lose It” in Diet Simple),
* Reward your successes (see “Get Sexy Lingerie” or “Kiss Your Spouse” in Diet Simple),
* Arrange your environment to help, rather than hinder, you. Limit exposure to high-risk situations and create reminders for your resolutions (see all of Diet Simple!),
* Expect occasional slips in your resolutions (see “Lighten Up!” in Diet Simple). Studies of successful weight loss maintainers show they experience just as many stressors and slips as weight relapsers; no one’s perfect after all (sorry to disillusion you)! The maintainers pick them self up, dust themselves off, and start all over again!
* Cultivate social support (see all of Diet Simple!). Successful weight loss maintainers are more likely to cultivate support from friends, loved ones, or professionals. It does take a village!
The Battle of the Bulge is Won at the Margins. Sweeping Dietary Overhauls are Impractical and Don’t Work Over Time!
Shrewd, Small, Concrete Changes Which Can be Easily Incorporated into Your Daily Routine Lead to Success!
Music and poetry move me deeply, and in ways I don’t always understand. All we know is after hearing something, we feel so much better. I’ve made some selections that have made a difference for me and hope you enjoy them too.
A Chocolate A Day? Health Benefits of Chocolate De-Mystified
- At February 11, 2012
- By Katherine
- In Articles, News
 6
6
Is it true that a chocolate a day will keep the doctor away? That’s what many chocolate companies would like you to believe in their Valentine’s Day advertisements. While it looks like cocoa has many health benefits, the chocolates you buy from your local stores may impart little of those benefits.
Are you celebrating Valentine’s Day with chocolate? Do you care about chocolate’s health benefits? Tell me about it below in my “Comments” section.
The cacao bean, grown mainly in Latin America, Africa and Asia, is loaded with beneficial compounds. In fact, its early uses, dating back 3,000 years were mainly medicinal. They have ranged from curing fatigue, angina, constipation, dental problems (tartar removal), dysentery, gout, an “overheated” heart, skin eruptions, fevers, and seizures. One doctor in the 1500s found it made people “extraordinarily fat” if used frequently and so it was prescribed for the thin and weak, according to an article in The Journal of Nutrition. It has been highly prized for centuries, which is reflected in its scientific name, Theobroma cacao, meaning “Food of the Gods.”
Eurpoeans discovered cocoa in the 1500s and over the next few centuries, chocolate, which we know and love so well was born. In this century, chocolate (processed cocoa with added fat, milk and sugar) has been enjoyed for its melt-in-your mouth texture and flavor, with its health giving properties largely forgotten by the civilized world, until recently.
In 1997, Harvard professor Norman K. Hollenberg published a landmark epidemiological study focused on cocoa. He found that high blood pressure was a rarity among Panama’s Kuna Indians who also didn’t experience the typical age-related increases. He at first attributed it to genetic protection. But, when the Kunas migrated to Panama City, their blood pressure increased, pointing to an environmental cause. Upon examination, Hollenberg found the Kunas drank large amounts of indigenous, unprocessed cocoa. Subsequent experiments conducted by Hollenberg and others, have found that cocoa, if high in flavanols, the beneficial plant compounds scientists believe impart most of cocoa’s benefits, relaxes the blood vessels, an important protection against hypertension and heart disease.
In the past ten years, cocoa research has intensified, mainly due to the largess of companies like Mars, Inc, most famous for Milky Ways and M&Ms. What’s striking is that candy companies, such as Mars and Nestle’s, have hired respected nutrition scientists and have been largely responsible for the advancement of cocoa research. Mars has collaborated with such institutions as Harvard, the University of California at Davis, and even the United States Department of Agriculture’s Agricultural Research Service. Through their research and others, many interesting discoveries about cocoa’s health benefits have been made.
The flavanols in cocoa help maintain a healthy vascular system, relax blood vessels, they reduce blood clotting – an aspirin-like affect –reduce oxidative damage, and improve blood flow. A study in the American Journal of Clinical Nutrition found cocoa also reduces inflammation. All of which reduces heart disease risk.
There have been some suggestion that flavanols can be used to treat vascular diseases like dementia, pre-eclampsia in pregnant women, and anything related to blood flow. Emerging research is looking into cancer as well.
But what about that chocolate bar in your vending machine? Are there any health benefits there? The answer: probably not much.
Most research about chocolate’s health benefits have used unsweetened cocoa or specially formulated high-flavanol chocolate. Unfortunately, these compounds are rarely in the chocolate we eat in 21st century America. Flavanols impart a bitter taste so they’ve been removed from most popular products to improve their flavor.
Most of the flavanols are in the cocoa beans and the level decreases with each processing step when it goes from the bean, to the cocoa powder and ultimately a finished chocolate product.
Since flavanols and their health benefits are a new discovery, chocolate companies are just beginning to see if there are ways to keep flavanols consistently high, but still have a tasty, popular product.
Katherine’s Chocolate-for-Health Tips
If you’re eating chocolate for health benefits, try my Dark Chocolate-Dipped Fruit recipe, for one, and be very discriminating in your selections.
You’ll get more flavanols, and therefore health benefits, with less processing. The first choice is cocoa, which isn’t Dutch processed – as when cocoa is “Dutch processed with alkali” the flavanols are reduced. Look for chocolate which has the highest percentage of cocoa as possible and to save calories, look for chocolate with lower fat and sugar levels. In general, cocoa is your best first choice. Second choice is a semisweet or bittersweet chocolate with a high cocoa percentage. Some chocolates go as high as 85% cocoa, but legally can be as low as 35%. I recommend no more than an ounce a day, which may be about 110 – 150 calories, depending on the chocolate. Any more than that and you’re probably going to take in too many calories for weight control.
The numbers:
Type of Chocolate Mg Flavonols Calories
1.3 oz Dark Chocolate Bars, Average*: 82 mg 187
1.3 oz Milk Chocolate Bars, Average*: 42 mg 198
1 TBSP Unsweetened Cocoa Powder, Average*: 75 mg 12
*USDA’s Nutrient Data Laboratory
Use this incredible chocolate fondue recipe for berries, sliced pears, bananas, or any favorite fruit!
Katherine’s Hot Cocoa:
1 tsp or 1 Tbsp unsweetened cocoa, to taste
1 tsp or 1 Tbsp honey
1 cup Skim Milk or 1% Milk or Soy Milk
Heat in microwave for 2 – 3 minutes and stir to blend the chocolate.
Using 1 teaspoon of cocoa and sugar, contains approximately 25 mg flavanols and 115 calories (zero saturated fat), depending on the milk used.
Using 1 Tablespoon of cocoa and sugar, contains approximately 75 mg flavanols and 153 calories
Are you interested in chocolate’s health benefits? How much chocolate do you eat? Let me know in my “comments” section below…